Ever wondered what makes your ride’s transmission so smooth? If not, you are not the first one Well, the mastermind behind the scenes for your smooth and seamless experience is “Torque Converter”. Think of it as your middleman who takes raw power from the engine and transfers it into wheels smoothly.
Truth be told, Torque Converter doesn’t sound that interesting at all. Well, with this blog you will change your opinion of it, as in this blog we are going to learn about the following:
- What is a Torque Converter?
- About Torque Converter Clutch
- Torque Converter Working Principle
- Parts of Torque Converter
- Working of a Torque Converter
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Torque Converter
- Torque Converter Vs Fluid Coupling
What is Torque Converter?
An Auto transmission torque converter is a type of fluid coupling that acts as a middleman between the engine of a vehicle to the transmission, it transfers rotational power from the engine to the transmission. It replaces the mechanical clutch in an automatic transmission. The main function of it is to allow the load to be isolated from the main power source. It sits in between the transmission and the engine.
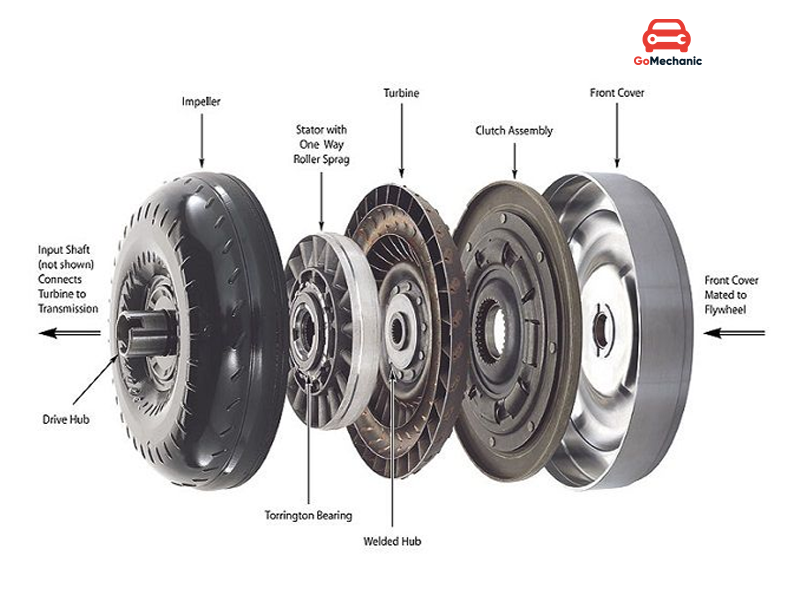

Auto gearbox torque converter functions similarly to clutch in the manual transmission system but as you might have guessed they are not that simple. They work using many forces of physics and their work is quite honestly beautiful. They prevent the car from stalling when it is stopped similar to clutch in a manual transmission.
About Torque Converter Clutch
The Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) mechanically locks the engine to the transmission by connecting the impeller with the turbine through a wet clutch. This action eliminates torque converter slip, increasing efficiency and reducing heat dissipation in automatic transmission fluid. There are several ways of locking the torque converter clutch. These differences are a function of the hydraulic circuit controlling the clutch actuation.
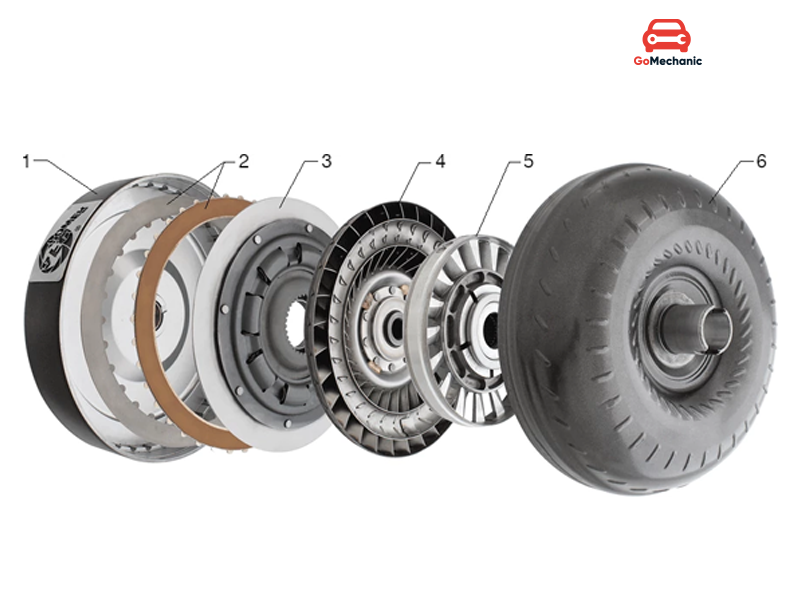
There are types of torque converter clutches, which controls oil flow through the torque
- Two-passage (2-pass) torque converter clutch
- Three-passage (3-pass) torque converters clutch
- Four-passage (4-pass) torque converters clutch
How Torque Converters Work?
Understanding the torque converter gearbox working principle is key, to understanding its importance in automatic transmission let’s take two fans. Imagine, one fan is connected to the power source while the other is not. When the powered fan begins to spin, the air generated from it causes the other fan to move as well. The air from the first fan strikes on the blades of the second fan and it also starts rotating almost at the same speed as the first one. When the second fan is stopped, it does not stop the first one. The first fan keeps rotating.
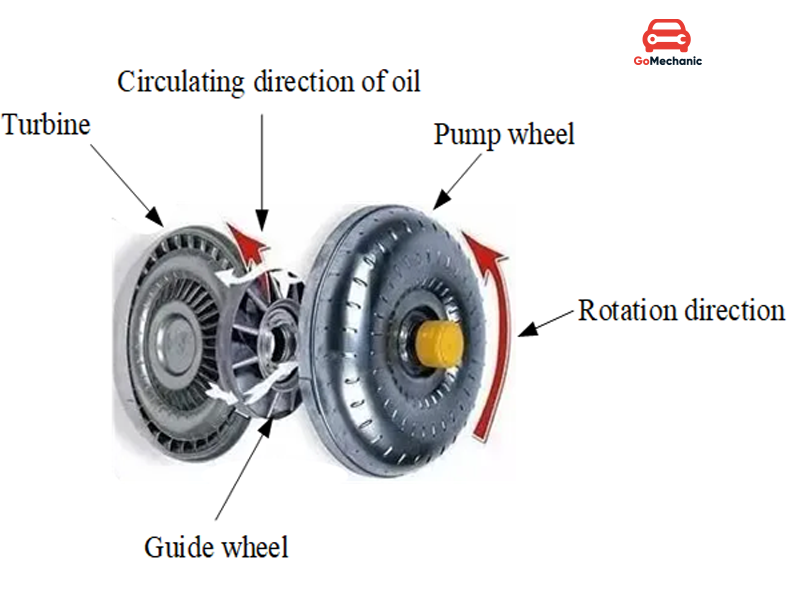
Similarly, in the Torque Converter Working Principle, the pump acts as the first fan which is connected to the engine, and the turbine acts as the second fan which is connected to the transmission system. When the engine runs, it rotates the pump and due to the centrifugal force, the oil inside the torque converter is headed toward the turbine. The turbine starts rotating as soon as the oil hits it which in turn makes the transmission system rotate and the wheels of the vehicle move. When the engine stops, the turbine also stops rotating but the pump connected to the engine keeps moving and this prevents the killing of the engine.
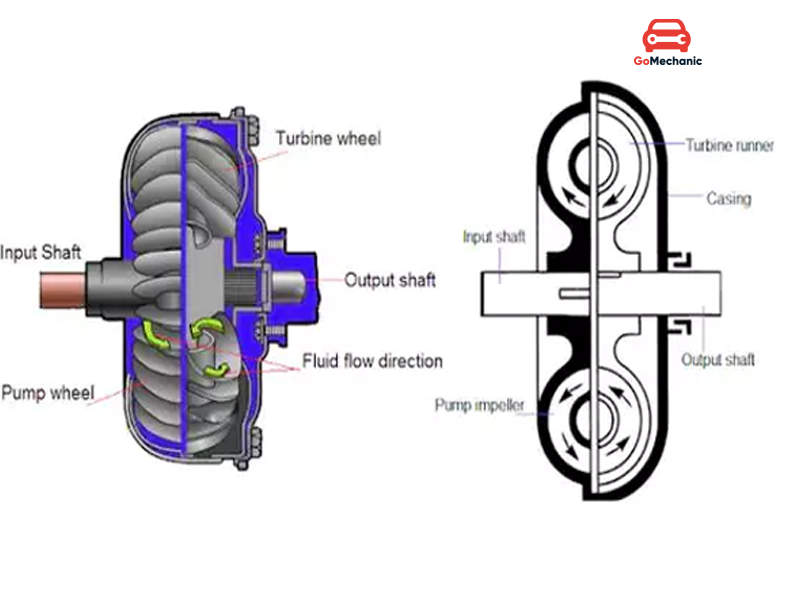
Parts of Torque Converter.
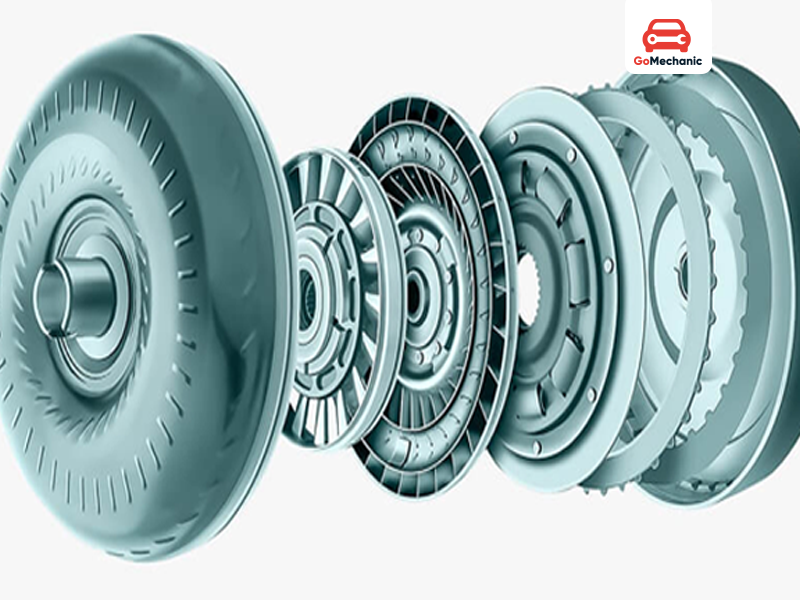
The auto transmission torque converter is an assembly of multiple parts and going straight to the working will make things complicated. To make the explanation more manageable we will divide the parts and learn their working individually then see how they work overall to become a fully functional torque converter.
- Impeller or Pump – The Impeller is attached to the container of the torque converter, which is also connected to the flywheel. It moves the fluid inside the container in the opposite direction of the casing’s rotation
- Turbine – The turbine powers the output shaft and is present in front of the pump closer to the flywheel. It rotates in an opposite direction to what the fluid is rotating to absorb the torque and make the output shaft move.
- Stator – Stator’s job is to ensure the fluid direction is correct after it comes out of the turbine. The correct direction, in this case, is the same as the direction of the pump.
Working of Torque Converter
The Torque converter principle comes to life when the flywheel from the engine is connected to the casing of the torque converter. This makes the entire casing rotate at the same RPM as the engine. The pump is connected to the casing and thus rotates with the same rpm and direction. There is fluid present inside the casing which is thrown around by the pump using centrifugal force. This fluid then goes towards the turbine which has small grates in it. These grates allow the fluid to go in and move the turbine. The turbine absorbs the torque and starts to rotate. The turbine is connected directly to the output shaft.
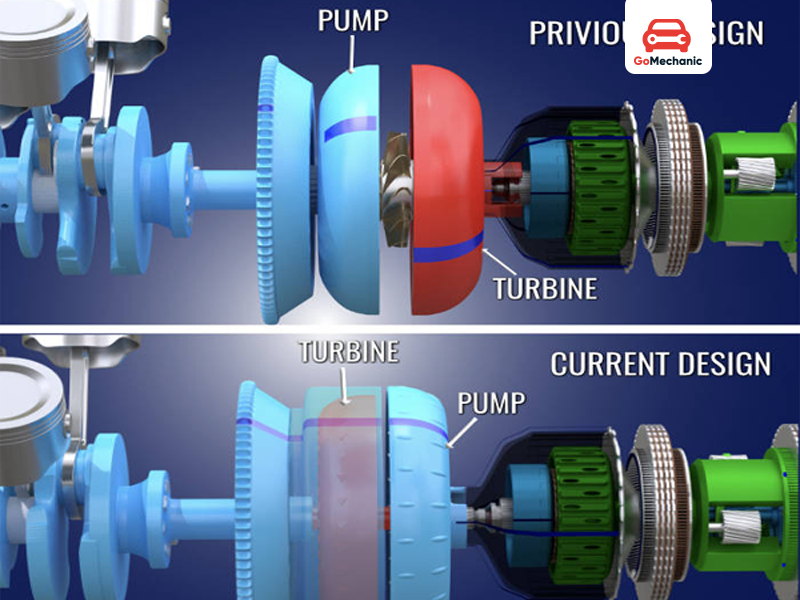
After the fluid comes out of the turbine it has almost no momentum left and is in the wrong direction of what the pump wants it to be. Hence the stator is used. It rotates the direction of the fluid and makes it similar to what the pump requires. This concludes the cycle which keeps on rotating to move the car.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Torque Converter
There are several advantages of using an auto transmission torque converter in vehicles. Despite its advantages, the torque converter automatic transmission is not without its drawbacks as well. Let’s understand both sides of the Advantages and Disadvantages of Torque Converters.

Advantages:
- Torque converter varies gear ratio in the range of 3:1 to 1:1 in infinite no. of stages which gives uniform acceleration.
- It produces the maximum torque as compared with the vehicle equipped with a clutch.
- It removes the clutch pedal.
- It makes the job of driving a vehicle easier.
- It allows the starting & stopping of the vehicle without any difficulty
- It provides driving comfort to drivers by avoiding manual interference of gear changing.
Give this a read – RPM Full Form and Meaning Explained: Everything you need to know
Disadvantages:
- The efficiency of the torque converter is high only within narrow limits of speed
- There is a chance of cavitation
Applications of Torque Converter
The Auto transmission torque converter is primarily used in vehicles with automatic transmissions but is also found in industrial applications such as forklifts etc.
- The torque converter is used in the vehicle that is equipped with an automatic transmission. It is also used in industrial power transmissions such as conveyor drives, winches, drilling rigs, almost all modern forklifts, construction equipment, and railway locomotives.
- It is used in marine propulsion systems.
This might pique your interest – 4WD vs AWD Explained: What You Must Know to Pick the Best Drive System
Torque Converter Vs Fluid Coupling
While both the Torque converter and Fluid Coupling are designed for similar purposes there are several differences among them as well. Here’s a breakdown:
| Torque converter | Fluid coupling |
| The main components are the pump, stator, and turbine. | The main components are the impeller and runner. |
| It is a torque multiplication unit. | It is simply a means to connect driving and driven members. |
| The turbine blades are inclined to have pitch. | Blades are merely fins. |
| It acts as an automatic clutch and serves the purpose of an automatic gearbox to increase torque. | It serves the purpose of an automatic clutch. |
| It is not as efficient as fluid coupling at highway speeds but is slightly more efficient under load. | It is efficient at highway speeds. |
| It is usually used in conjunction with an automatic clutch (mostly fluid flywheel) to eliminate the slight loss of efficiency at highway speeds. | It is not assisted by a friction clutch. |
| It never locks up and the flow of oil never stops but continues. | The impeller and runner are locked up and the movement of oil stops during engagement when centrifugal force is approximately the same on both members. |
In the end, a Torque converter is the unsung hero of your car’s automatic transmission system. It acts as a middleman between the engine and the transmission, making sure that your ride is smooth and soothing.
FAQs
1. What are the symptoms of a bad torque converter in an automatic transmission?
There are various signs to detect a bad torque converter. But few of them are quite primary such as loss of acceleration, slipping between gears, transmission overheating, and if transmission fluid is leaking.
2. How much does it cost to replace a torque converter?
It can be quite expensive. However, there is no fixed cost. It totally depends upon your needs and requirements.
3. What is the torque converter in the automatic gearbox?
A torque converter provides the same function in an automatic vehicle as a clutch in a manual vehicle – allowing the engine to keep running as the wheels come to a stop.
4. What are the symptoms of a bad torque converter?
A faulty torque converter can cause delayed acceleration and jerky movement. You may feel shuddering at certain speeds; instances such as overheating and poor fuel efficiency are also common signs.
5. Which is better CVT or torque converter?
Torque converters are known for smooth performance and durability. CVTs offer better fuel efficiency but can feel less responsive. For long-term reliability, torque converters are often preferred.
6. Which is better, a torque converter or DCT?
Torque converters are more forgiving and last longer in traffic-heavy conditions. DCTs offer faster shifts and better performance but require careful maintenance. Indian driving conditions favour torque converters.
7. How much does it cost to replace a torque converter?
Replacement is expensive. Costs can range from ₹50,000 to over ₹1.2 lakh depending on the car. Labour and transmission work add to the cost.
Others Read – Conversion of Petrol Car to CNG: Shift to a Cleaner, More Cost-Effective Fuel






Hi
Excellent article. Super quality pictures and clear explanations of a complex transmission part.
Well done. Very helpful and good insight article.
Thanks.
Thanks for the appreciation!
Excellent explanation
Reality your explain has been a great one to those who can understand