In the automobile sphere, there is one very silent yet immensely powerful ingredient that binds everything together, and that will always be the chassis. If the heart is represented by the engine and the legs by the four wheels, then a chassis will be the backbone giving stability, strength, and support to the entire framework of the particular automobile. The chassis decides the performance of the vehicle as we see it, be it a super compact city car, a SUV, or a super-sleek sports car. But what does a chassis mean for your driving experience?
What is a chassis?
In very simple terms, it is the frame of the car, the basis of everything else. All those structural elements supporting the body, the engine, the transmission, the suspension, wheels, and other primary components comprise the chassis. It is like a skeleton giving shape, rigidity, and strength to your car. More commonly, the term chassis may refer simply to the frame, but there is a fine distinction. The chassis is referred to as the entire bottom structure, whereas the frame refers to the primarily grounded main support member forming the chassis.
Chassis vs. Frame: Understanding the Difference
| Aspect | Chassis | Frame |
| Definition | The entire structure that supports the vehicle’s body, engine, suspension, and other components. | The primary structural component, typically the rigid part, of a chassis. It forms the base of the vehicle. |
| Components | Includes the frame, suspension, engine, transmission, wheels, and other vital elements. | Primarily just the rigid skeletal structure to support the body and other components. |
| Design Type | Can be Monocoque (integrated body and frame) or Body-on-Frame (frame with body attached). | Generally refers to the structure in Body-on-Frame designs where the frame is separate from the body. |
| Common Uses | Found in most modern cars (particularly monocoque) and electric vehicles. | Common in trucks, SUVs, off-road vehicles, and older car designs. |
| Weight | Typically lighter in Monocoque chassis due to integrated design, but can be heavier in Body-on-Frame. | Usually heavier because it is a separate structure that must support the body. |
| Flexibility | Offers more flexibility in terms of design (particularly in Monocoque). | Less flexible and more rigid, offering better support for heavy loads. |
| Crash Safety | Monocoque provides superior crash protection due to its unified design. | Generally more rigid but offers less crash protection compared to Monocoque. |
| Cost and Production | Typically more cost-effective in mass production (especially for monocoque). | More expensive to produce and heavier in mass production. |
| Performance | Provides smoother ride and better handling due to integrated design. | Better for off-road and heavy-duty vehicles as it can endure heavy loads and tough terrain. |
| Manufacturing Process | Easier to mass-produce in modern vehicles, especially with Monocoque. | More complex and heavier to produce, often requires more labor for assembly. |
Materials: What Is the Chassis Made Of?
Great structures set the tone for chassis construction; hence, their materials are of pivotal importance. Directly, such materials affect the weight, strength, cost, and durability of motor vehicles.
- Steel is aimed at mass production for vehicular purposes. This is a very strong, durable, and economically feasible material. Steel chassis have been rolled and welded being best for mass production and are ideally suited for high-end vehicles. Steel is heavier than other materials, but, when it comes to balancing strength with price, it fills the golden mean and affords excellent structural strength and safety to its application.
- Aluminum offers a good mix of strength and weight saving benefits; it is lighter than steel. It is generally applied to sports cars to eliminate weight for better efficiency without almost any loss in strength. It is an expensive material, much more than steel, but surely makes a significant contribution toward fuel-efficient and handling.
- Carbon fiber is the king of the materials for high-performance cars and supercars. It makes for an extremely light, strong, and rigid material, truly for those after maximum speed and handling. However, on the other hand, carbon comes with a huge price and is extremely difficult to manufacture. So its use is largely restricted to premium, low-volume cars or race cars.
How the Chassis Affects Your Driving Experience
The experience on handling, riding, or feeling on road is intensely dependent on the chassis. Chassis design has a big contribution to excellent and smooth handling, stability in cornering, and general riding comfort.

- Handling and Rigidity: The rigidity of a chassis means some resistance to twisting and bending, thereby allowing suspension and wheels to perform their functions better. Flexibility in a chassis creates problems during acceleration or cornering; instability will ensue, hence losing control during the ride. The best chassis will provide the required torsional rigidity to maintain alignment and traction of your car for precise handling.
- Ride Comfort: The comfort and luxury provided on your ride may very well depend on the chassis. Good chassis design reduces vibrations, bumps, and noise, giving seamless functioning on the road. Poor design results in bumpy uncomfortable rides where outside vibrations seep into the cabin.
- Safety: Performance is not the only area influenced by the chassis in a car; it is also an important part of your car’s safety. A monocoque chassis would offer the best protection in case of a crash owing to its unity in the structure, which absorbs the impact better. The body-on-frame chassis would be better in dealing with harsh conditions, thus offering safety by strength and resistance to deformation.
Electric Vehicles And The Chassis
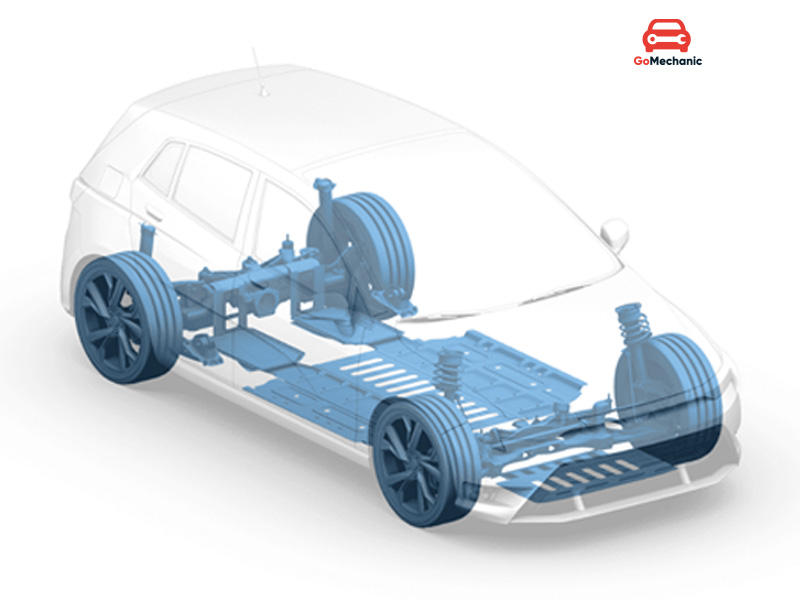
With the boom of electric-powered automobile design, the concept of chassis has been redefined. Nowadays many companies building EVs opt for a platform termed a “skateboard.” This chassis configuration is characterized by a flat, very low base which contains the battery pack and electric motors. This compact and efficient layout enables maximum creativity in vehicle design, providing ample room for the passenger cabin while keeping the weight distribution reasonable for performance. Given the flexibility in accommodating a wide range of electric vehicles-from smaller cars to an even larger SUV-the skateboard platform very much retains the prime merit of electric mobility in terms of efficiency and sustainability. A chassis can be considered the least appreciated part of the car. Not many will know much about them, and even fewer will care. Admittedly, we do not have an option to decide which chassis will go into our car, but understanding them will give you an insight into your car’s potential and limitations. There are four types of car chassis mainly defined.
Check out: How Are Cars Classified According To Body Type?
Types of Car Chassis
-
Ladder Frame Chassis

One of the oldest chassis, the ladder chassis gets its name from the shape of has which simply put, is like a ladder. It has two long and heavy beams which are supported by two short beams. The main selling point of the ladder chassis was how easy it was to manufacture. During the beginning of the era of the automobile, technology was not really advanced and the simplicity of the ladder chassis made it easier to mass-produce. The chassis also makes the car assembly easier. The ladder chassis is quite heavy and thus still finds use in vehicles that need to tow heavy stuff around.
Download the GoMechanic App Now!
Advantages
- Easier to assemble as parts can be easily put in.
- Construction method makes it quite tough.
- Easier to fix as parts are not permanently attached.
Disadvantages
- The ladder chassis has a weak torsional rigidity making it bad for cornering.
- Heavyweight makes it not ideal for sports cars or hatchbacks.
-
Backbone Chassis

It also gets its name from how it’s constructed. A rectangular cross-section cylindrical tube through the middle of the chassis that connects the top and the bottom suspension. The backbone. It’s present in cars like Skoda Rapid and DMC DeLorean. The cylindrical tube actually covers the driveshaft thus making it safer from getting damaged which can also be a disadvantage.
Read How much Ground Clearance is Good Ground Clearance in India?
Advantages
- Due to its construction, the half axle has better contact with the ground when off-roading.
- The driveshaft is covered by the chassis makes it more likely to survive off-roading.
- The structure has good torsional rigidity allowing it to withstand more twist than ladder chassis.
Disadvantages
- The driveshaft repair is complicated if it fails as the main chassis covers the entire shaft which makes it necessary to open it.
- The manufacture of backbone chassis is quite expensive which increases the cost of cars it is in.
-
Monocoque Chassis

A unibody structure, it too gets its name from its structural look. Monocoque being french for ‘single shell’ or a ‘single hull’. The monocoque was first used by ships and then by aeroplanes. It took quite some time to figure out that they can be used in cars as well. A monocoque is a shell around the car made by using both chassis as the frame in a single construction. This is the most commonly used chassis right now due to the number of advantages of has over the other two chassis.
Advantages
- It’s safer than both the other chassis due to its cage-like construction.
- The chassis is easy to repair as well.
- It has superior torsional rigidity.
Disadvantages
- The chassis is obviously heavy as it’s both the frame and chassis as one single entity.
- Producing it in small quantities is not financially feasible and thus it cannot be used for cars that are not mass-produced.
-
Tubular chassis

Tubular chassis were mainly used in race cars due to the unrivalled safety they provide. These were an upgrade from the ladder chassis as they were three dimensional and were stronger than ladder chassis. They employed the use of a strong structure below the doors to get more overall strength. Tubular chassis are rarely used on passenger cars.
Advantages
-
- Better rigidity compared to other chassis in the same weight.
- Offers the best weight/rigidity ratio allowing the car to be lightweight while being strong.
- Best choice for race cars due to lightweight and better rigidity than other chassis.
Disadvantages
-
- Tubular chassis are complex structures and cannot be made using autonomous methods.
- Tubular chassis are time-consuming to build and cannot be mass-produced.
- Not feasible to be used on passenger cars.
- The structure raises the door which makes it difficult to access the cabin.
Also Read: Transmissions: Manual vs CVT vs DSG vs AMT Explained!
Future Trends in Automotive Chassis Design:
- Lightweighting with Advanced Materials
Future chassis design will focus primarily on lightweighting, which is essential in terms of improving fuel efficiency, handling, and vehicle performance overall. Electric vehicles (EVs) and performance are other buzzwords in automotive terminology that all manufacturers are tapping into with use of future technologies such as carbon fiber, magnesium alloys, or high-strength steel composites.
- Modular EV Platforms
With growing acceptance of electric vehicles, the modular EV platforms will completely redefine how chassis is designed and produced. Rather, these skateboard platforms will emplace components necessary to operate, such as batteries, motors, and drive systems, upon a flat and scalable base that could be used by different vehicle types. Such installation allows the manufacturer to offer efficiency and cost-effectiveness through high flexibility and a scalable range in vehicle designs.
- Active and Adaptive Chassis Systems
Given that consumers’ expectations are changing, active and adaptive chassis systems will become standard in the next generation of vehicles. They allow the suspension and damping mechanisms to be automatically controlled to adapt to real-time road conditions, driving styles, and vehicle load. By actively optimising activity to a changing environment, active suspension systems give a comfortable ride, good handling, and improved safety. For example, these systems can be designed to detect potholes in the road and adjust itself to reduce impact, ensuring performance and comfort is optimized.
- Smart Technology Integration
With autonomous driving technology on the rise, automobile chassis design will naturally become more integrated and be part of what the future chassis will be all about. The future chassis would be designed with mounts to embed sensor systems for cameras, LiDARs, or radars, where built-in integration points are important for components relative to autonomous vehicle functionality. Moreover, smart connectivity would be very much incorporated in the future to make a vehicle talk to other systems internally and outside, to traffic infrastructures, and finally, to other vehicles. The backbone chassis would then also support these sophisticated technologies, ensuring that they could operate with maximal safety and precision without much compromise in seamless interaction with the environment.
- Sustainable Manufacturing
Sustainability-chassis design of the future. The chassis design would also be geared towards sustainable practices, restricting itself to environmentally friendly materials in the form of ending up in an eco-manufacturing process. Moving to recyclables, such as aluminum, steel, and even plastic composites, is one way that manufacturers are trying to shrink their ecological footprints. Sustainable production processes will also become the rule, such as going green in manufacturing processes that cut down waste and energy used and emissions.
- 3D Printing
It is expected to revolutionize chassis design with the lowest material waste, as with 3D printing technology, manufacturers will be able to construct sophisticated custom parts with minimum material wastage. 3D printing makes it possible to create lightweight, complex chassis components previously impossible with traditional means and could result in a lower time frame for developing prototypes and a streamlined production process.
Conclusion
To sum up, the chassis is much more than just an undercarriage of a vehicle; rather, it constitutes an actual framework which is responsible for the performance, safety, and comfort aspects of the car. The chassis provides structural integrity, while also affecting the driving experience; thus it can be considered as the backbone holding every other component in place. In view of emerging advancements such as lightweight materials, modular platforms, and adaptive systems, the chassis design promises even advanced features that enhance efficiency, safety, and sustainability. Whether driving the routine runabout, electric vehicles, or high-performance sports cars, knowledge about the role of the chassis endows an appreciation for the engineering marvel that makes contemporary vehicles safe, efficient, and a joy to drive.
This covers the three major types of car chassis. As you might have noticed all three have a different role to play and are useful for different types of driving styles. You can’t exactly compare them and decide which type is better because they are all individually good in what they do.
FAQs for the Blog “Types Of Car Chassis Explained | From Ladder To Monocoque!”
Q1. How many types of chassis are there?
There are several types of car chassis, including ladder frame, monocoque (unibody), backbone, and space frame.
Q2. Which Indian cars have ladder frame chassis?
Indian cars with ladder frame chassis include the Toyota Fortuner, Mahindra Thar, Force Gurkha, and Mahindra Scorpio-N.
Q3. Which chassis is best for a car?
The “best” chassis depends on the vehicle’s purpose. Monocoque chassis offer better handling and fuel efficiency, while ladder frames are more durable for off-road and heavy-duty use.
Q4. Can I replace the monocoque chassis of my car?
Replacing a monocoque chassis is impractical and often impossible, as it’s integral to the vehicle’s structure.
Q5. Which is better, ladder frame or monocoque?
Monocoque chassis are lighter and offer better handling, suitable for most cars. Ladder frames are sturdier, ideal for off-road vehicles and heavy loads.








Thank you
Good explanation. Thankyou.
Thanks for being an avid reader of the GoMechanic Blog. Stay pinned for everything automotive.
Awesome, awesome read
The study’s is enjoeble